2025/9/17大约 14 分钟
Java IO
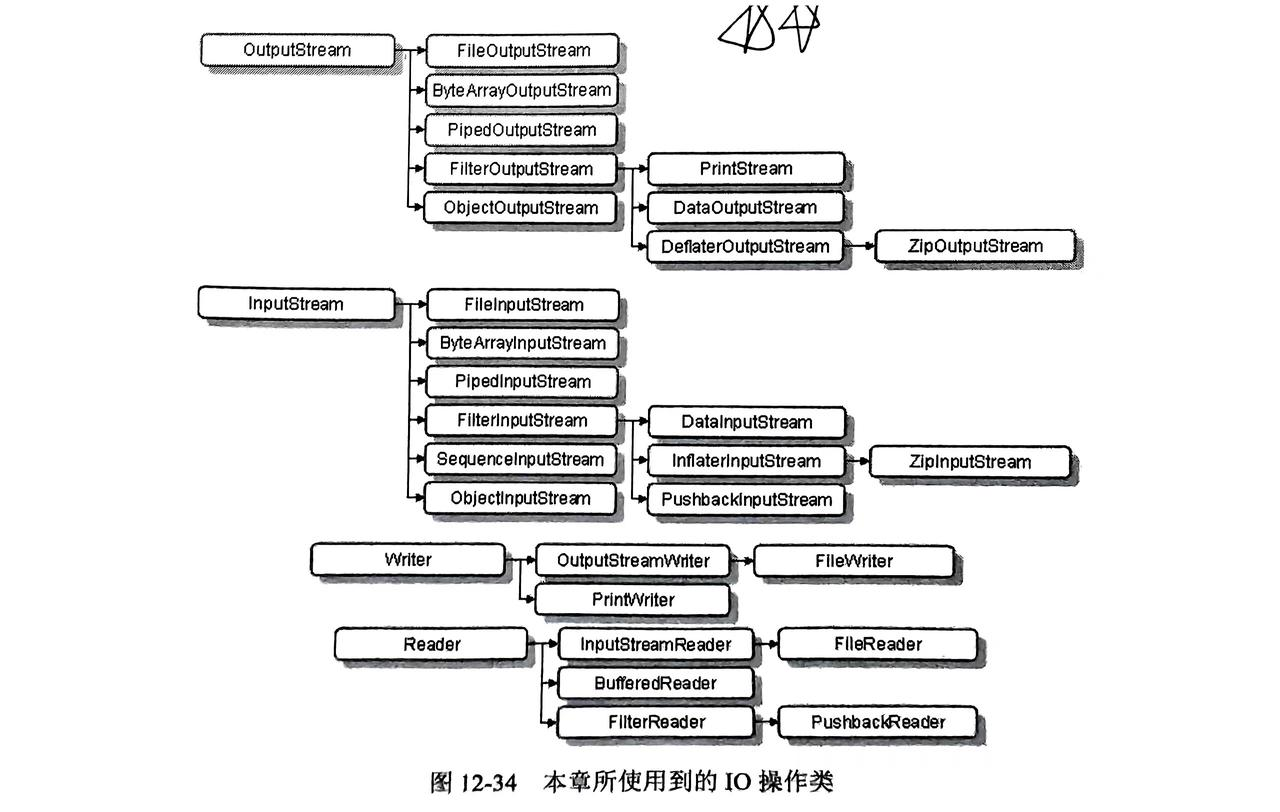
1. 继承关注图
2. 操作文件的类--File
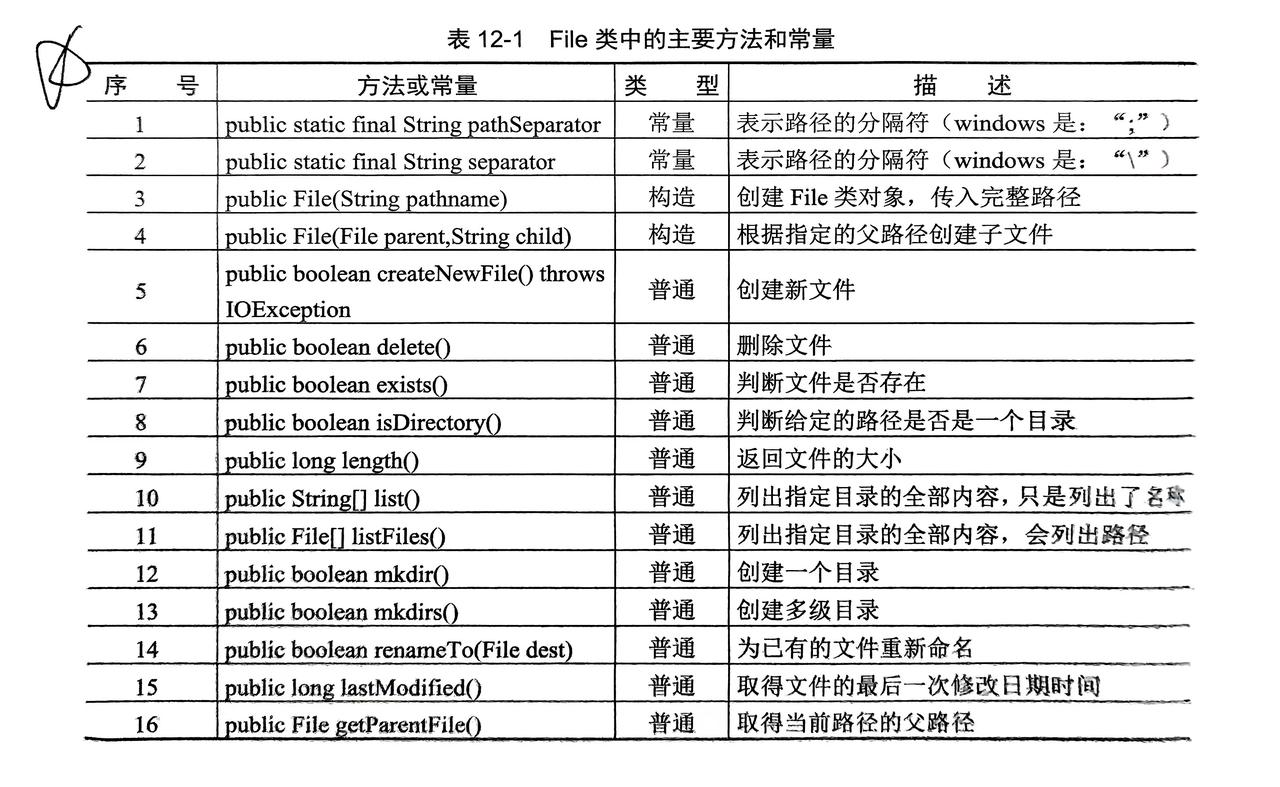
- 创建和删除等进行文件操作时,JVM 会造成一定的延迟
3. 字节流和字符流的基本操作
- 字节流主要操作
byte数组,字符流操作字符(两个字节)可以看做操作字符串 - 字节流中输入使用
InputStream类,输出使用OutputStream类 - 字符流中输入使用
Reader类,输出使用Writer类 - 输入输出是以程序为参照物:输入为输入到程序中(文件数据读到程序中),输出为输出写到文件中
3.1 字节流
3.1.1 字节输出流:OutputStream类
- 是所有 IO 中字节输出流中最大的父类
- 是抽象类需要子类来实例化使用(
FileOutputStream...等)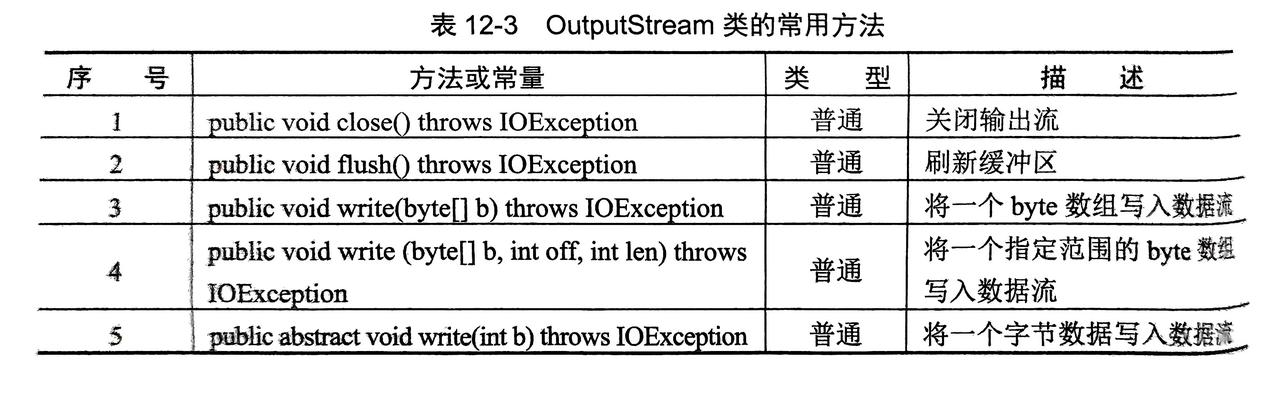
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取操作文件
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01");
// 子类实例化OutputStream流,传入需要操作的文件(设置追加写入外加参数true)
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file,true);
// 需要写入的字符串
String str = "Holle World";
// 转换为字节
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
// 遍历字节一个一个写入到文件里
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
outputStream.write(bytes[i]);
}
// 也可以直接写入一个byte数组,两种方法可以任意使用
outputStream.write(bytes );
// 关闭输出流
outputStream.close();
}
}3.1.2 字节输入流:InputStream类
- 是所有 IO 中字节输入流中最大的父类
- 是抽象类需要子类来实例化使用(
FileInputStream...等)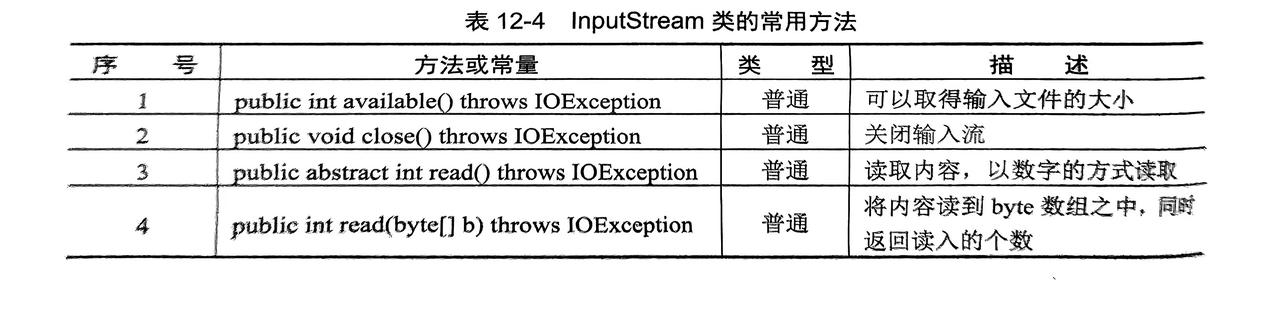
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取操作文件
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01");
// 子类实例化FileInputStream
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// 创建接收数据的字节数组
// 方法一:固定数组(固定长度使用的大量资源并可能导致数据接收不足)
// 方法二:获取file的长度并设置长度
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[1024];
byte[] bytes2 = new byte[(int) file.length()];
// 读取数据并返回长度
int len = fileInputStream.read();
fileInputStream.close();
System.out.println(new String(bytes1,0,len));
System.out.println(new String(bytes2));
}
}- 另外一种读取方法;
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取操作文件
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01");
// 子类实例化FileInputStream
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// 创建接收数据的字节数组
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[1024];
int len=0;
int temp=0;
// 一个一个读取放入temp,读到末尾返回-1
while ((temp=fileInputStream.read())!=-1){
bytes1[len]=(byte) temp;
len++;
}
fileInputStream.close();
System.out.println(new String(bytes1,0,len));
}
}3.2 字符流
3.2.1 字符输出流:Writer类
- 是一个抽象类,需要子类进行实例化(
FileWirter...等)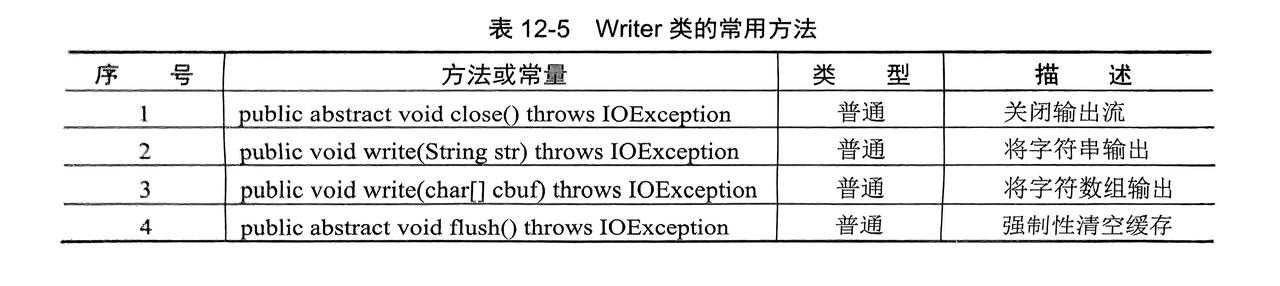
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取操作文件
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01");
// 子类实例化Writer
Writer fileWriter = new FileWriter(file,true);
String str = "hello world";
// 直接调用参数参数为字符串,也可以是char[]
fileWriter.write(str);
fileWriter.close();
}
}3.2.2 字符输入流:Reader类
- 是一个抽象类,需要子类进行实例化(
FileReader...等)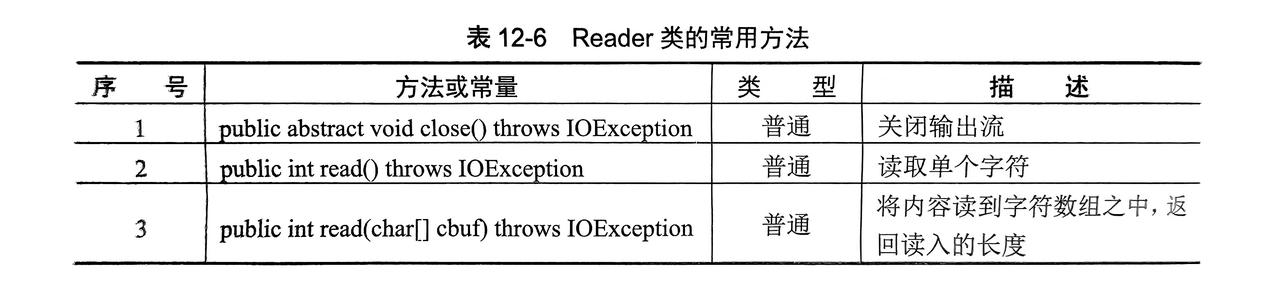
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取操作文件
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01");
// 子类实例化Reader
Reader fileReader = new FileReader(file);
String str="";
// 只能读取到char[]中
char[] chars=new char[(int) file.length()];
// 也可以循环读取(同字节输入流一样,把byte改为char即可)
fileReader.read(chars);
System.out.println(chars);
}
}4. 字节流与字符流的区别
- 字符流关闭输出流强制清空缓冲区到文件中,不关闭则不会写入到文件中
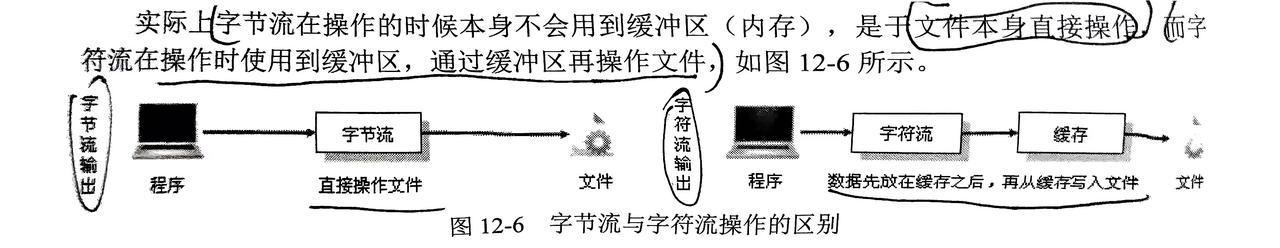
1.什么叫缓冲区?
解释:缓冲区可以简单理解将数据暂时读入到一块内存区域
2.使用字节流好还是使用字符流好?
解释:字符只在内存中才能形成,而所有文件在硬盘中或传输中都是以字节的形式传递,所以使用字节流好
5. 转换流
OutputStreamWiter输出转换流:Witer的子类,将字节流对象转换为字符流对象InputStreamReader输入转换流:Reader的子类,将字节流对象转换为字符流对象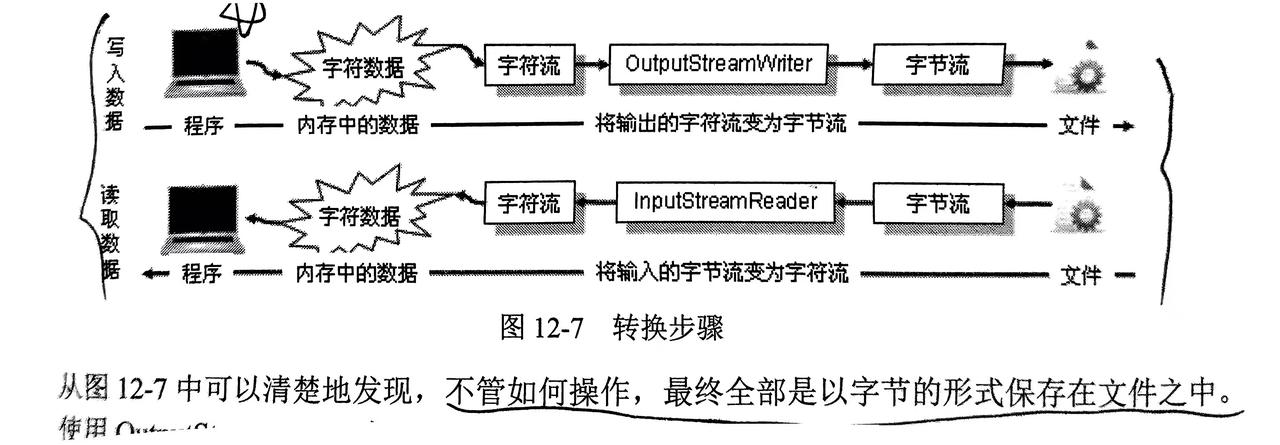
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取操作文件
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01");
// 子类实例化字节输出流
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file,true);
// 字节流转为字符流
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream);
// 字符流写出数据
outputStreamWriter.write("zijie");
outputStreamWriter.close();
}
}public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取操作文件
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01");
// 子类实例化字节输入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// 字节流转为字符流
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream);
char[] chars = new char[1024];
// 字符流读取
inputStreamReader.read(chars);
System.out.println(chars);
}
}6. 内存操作流
- 将内存当做一个临时文件,进行字节,字符的写入写出
- 字节内存流:
ByteArrayInputStream(内存字节输入流),ByteArrayOutputStream(内存字节输出流) - 字符内存流:
CharArrayReader(内存字符输入流),CharArrayWiter(内存字符输出流)
此时的写入写出要以内存为主视角(input 为写入内存,out 为读取内存)
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 准备需要写入的数据
String string = "Holle";
// 实例化内存字节输入流
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(string.getBytes());
// 准备内存字节输出流,接收数据
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int temp=0;
// 注意这里是input的变量读取数据
while ((temp= byteArrayInputStream.read())!=-1){
char c = (char) temp;
// 将内容从内存中取出来
byteArrayOutputStream.write(c);
}
String newStr=byteArrayOutputStream.toString();
byteArrayOutputStream.close();
byteArrayInputStream.close();
System.out.println(newStr);
}
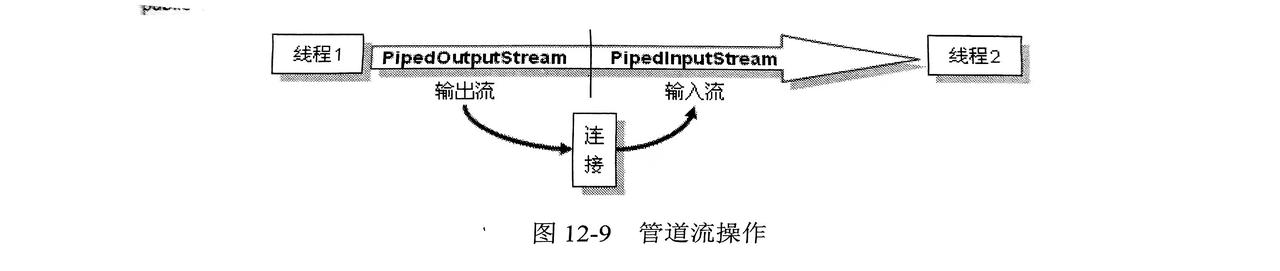
}7. 管道流
- 作用于:可以连接两个线程的通信
- 分为:
PipedOutputStream(管道输出流),PipedInputStream(管道输入流) - 要进行管道输出,必须将输出流建在输入流前面
// 发送方
public class Send implements Runnable{
// 管道输出流
private PipedOutputStream pos=new PipedOutputStream();
public PipedOutputStream getPos() {return pos;}
// 线程执行实现方法
public void run() {
String str = "Hello";
try {
// 传输信息
pos.write(str.getBytes());
pos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
// 接收方
public class Receive implements Runnable{
// 管道输入流
private PipedInputStream pis=new PipedInputStream();
public PipedInputStream getPis() {return pis;}
public void run() {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len=0;
// 接收信息
try {
len = pis.read(bytes);
pis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
}
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 实例化线程
Send send = new Send();
Receive receive = new Receive();
// 搭建管道(输出流后接输入流)
send.getPos().connect(receive.getPis());
// 启动线程
new Thread(send).start();
new Thread(receive).start();
}
}8. 打印流
- 打印流补足了
OutStream流只能输出字节的不足,PrintStream为OutStream子类 - 分为:
PrintStream(字节打印流),PrintWiter(字符打印流)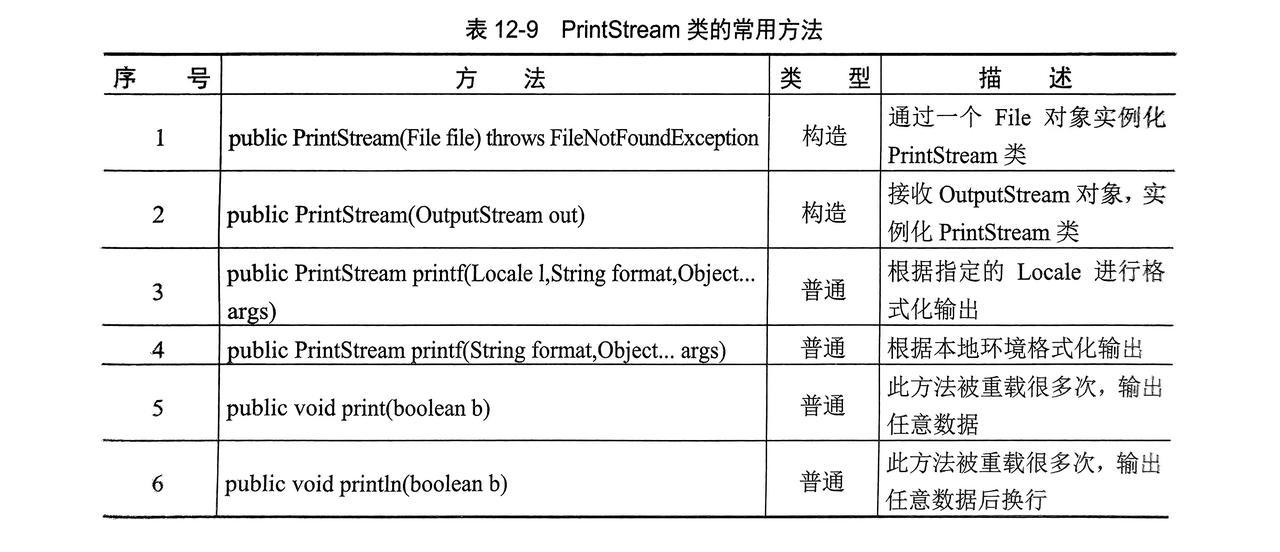
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取操作文件
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01");
// 实例化打印流
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(file);
// 写入数据
printStream.print("hello"+" World");
printStream.close();
}
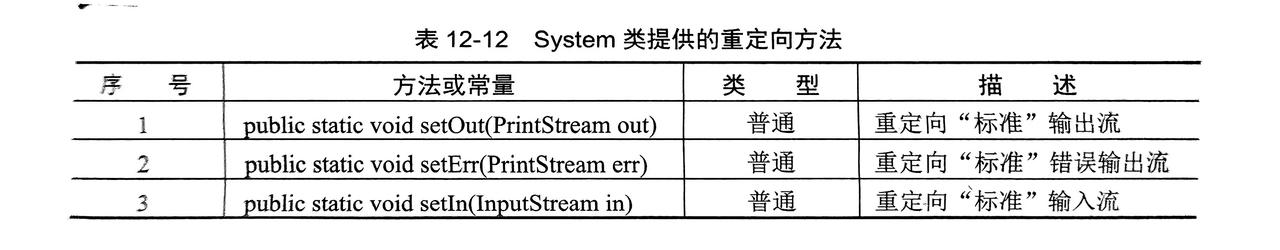
}9. System对IO的支持
- 在
System类中的err,out本身就是PrintStream的实例化对象,而in是InputStream的实例化对象
9.1 System.out
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// System.out本身是向屏幕输出的,给到实例化OutPutStream父类时也是
// System.out本身PrintStream,OutputStream为其父类可以实例化
OutputStream out = System.out;
// 屏幕输出hello
out.write("hello".getBytes());
}
}9.2 System.err
- 用于打印错误信息
try {
OutputStream out = System.out;
out.write("hello".getBytes());
}catch (IOException e){
System.err.print(e);
}相较于System.out都是打印有什么不同吗?
out是用于给用户看到的,而err是专门打印错误信息,用于后台打印,不希望用户看到
9.3 System.in
- 用于键盘输入信息,是
InputStream的实例化对象 - 同样的
System.in的接收对象是键盘输入
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 实例化InputStream,System.in接收的对象为键盘,则InputStream也是
InputStream in = System.in;
// 接受信息变量
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
System.out.println("请输入信息:");
// 读取信息,也可以不要固定变量,而使用循环一个个读取添加到StringBuffer中
// 因为是一个个读取会出现中文是乱码,则需要BufferedReader来解决
int len = in.read(bytes);
System.out.println("输入的信息为:"+new String(bytes,0,len));
}
}9.4 输入\输出重定向
- 重新定义输入输出的来源或去向
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 设置重定向的路径
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01");
// 对System.in重定向,来源设置为文件中的内容
System.setIn(new FileInputStream(file));
// 再赋值给InputStream
InputStream in = System.in;
// 接受信息变量
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
System.out.println("请输入信息:");
int len = in.read(bytes);
System.out.println("输入的信息为:"+new String(bytes,0,len));
}
}提示:建议不要对err进行重定向
因为原则上需要 err 是不能对用户所见的!
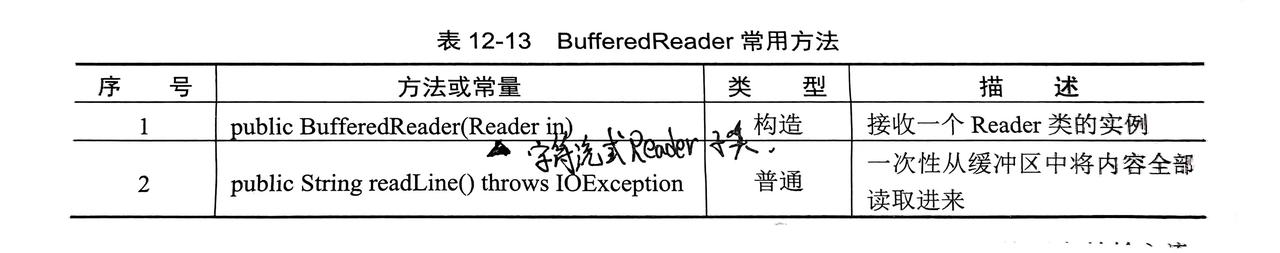
10. BufferedReader类
- 将所有读取的字节都存放到缓冲区,然后从缓冲区中读取数据
提示:
因为 BufferedReader 类只能接受字符流,如果需要键盘 System.in 输入时,需要进行转换

public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 实例化BufferedReader类
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("请输入信息:");
// 等待读取信息
String str = bufferedReader.readLine();
System.out.println("输入的信息为:"+str);
}
}11. Scanner类
- Java 提供的专门输入数据的类
Scanner可以接收任意的输入流(InputStream)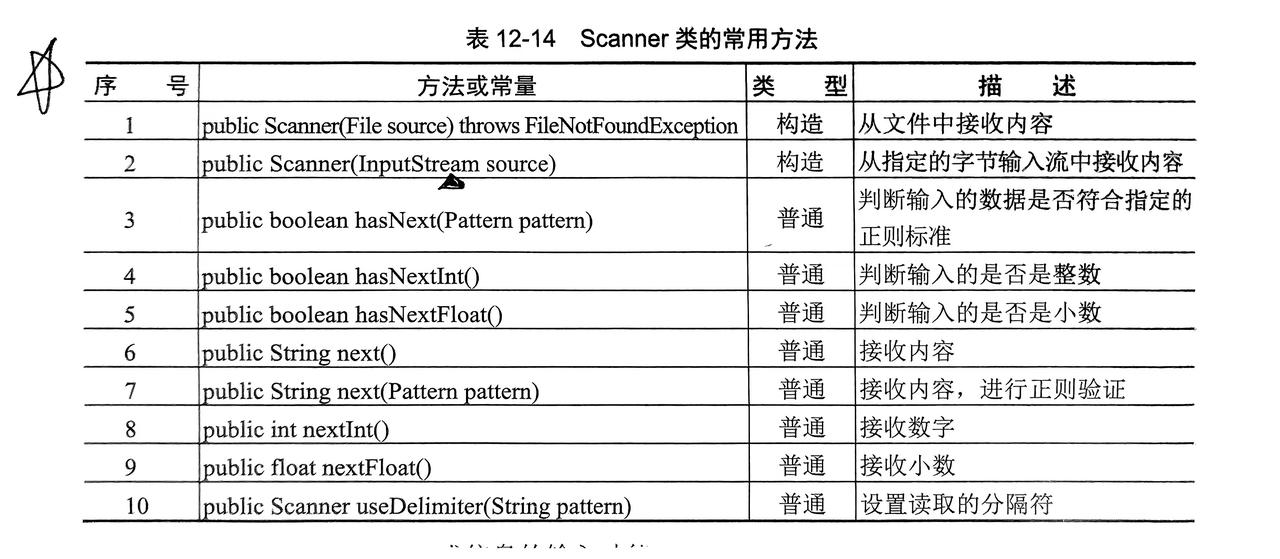
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 实例化Scanner类,并接收System.in键盘输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入信息:");
// 等待接收数据
String str = scanner.next();
System.out.println("输入的信息为:"+str);
}
}提示:Scanner默认的分隔符为空格,所有当数据中出现空格则会中断:
可以在输入之前使用 useDelimiter("\n") 修改为回车!
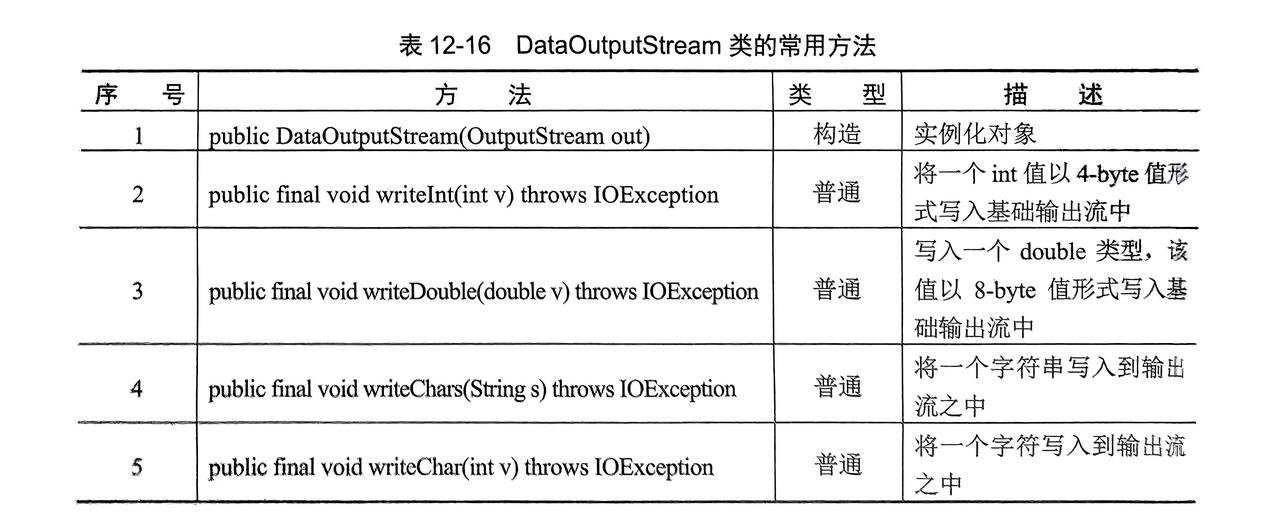
12. 数据操作流(了解)
- 自我理解:就是指定写入数据的类型(
int,float,char...),读取时可以根据这些类型读取 - 分为:
DataOutPutStream(数据输出流),DataInputStream(数据输入流) - 继承了
FilterOutPutStream同时实现了DataOutPut(数据输出接口)
12.1 DataOutPutStream
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 路径
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file03.txt");
// 实例化数据输出流
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
String[] names={"衬衣","手套","围巾"};
float[] prices={54.1f,45.1f,12.3f};
int[] nums={3,2,1};
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
dos.writeChars(names[i]);
dos.writeChar('\t');
dos.writeFloat(prices[i]);
dos.writeChar('\t');
dos.writeChar(nums[i]);
dos.writeChar('\t');
}
dos.close();
}
}12.2 DataIntputStream
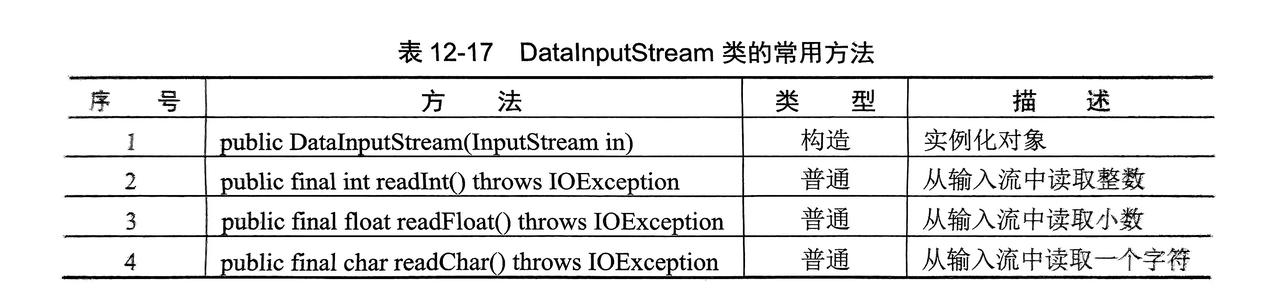
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 路径
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file03.txt");
DataInputStream dis =new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
try {
char c = 0;
while (true) {
char[] temp = new char[200];
int len = 0;
while ((c = dis.readChar()) != '\t') {
temp[len] = c;
len++;
}
String name = new String(temp, 0, len);
float price = dis.readFloat();
dis.readChar();
int num = dis.readInt();
dis.readChar();
System.out.printf("名称:%s;价格:%5.2f;数量:%d\n", name, price, num);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
try {
dis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}13. 合并流
- 将两个文件合并为一个文件
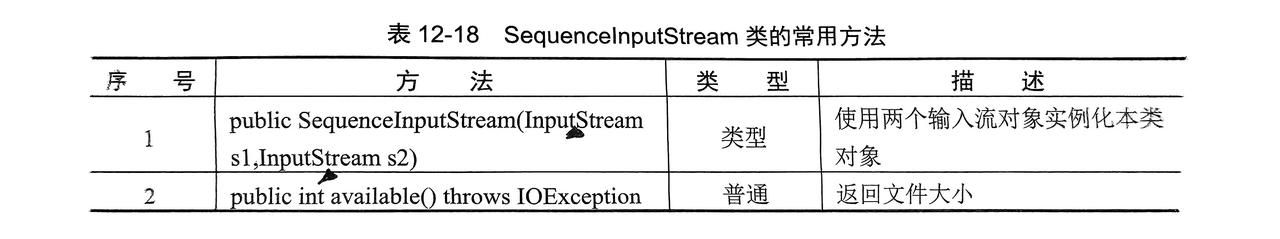
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1,2,为需要合并的文件,3为合并后的文件
File file1 = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01.txt");
File file2 = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file02.txt");
File file3 = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file03.txt");
// 实例化输入流和输出流
InputStream in1 = new FileInputStream(file1);
InputStream in2 = new FileInputStream(file2);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file3);
// 实例化合并流,合并顺序和参数数据一致
SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(in1, in2);
int temp=0;
// 读取写入
while ((temp=sis.read())!=-1){
char c=(char) temp;
out.write(c);
}
sis.close();
out.close();
in1.close();
in2.close();
}
}14. 压缩流
14.1 压缩
- 将文件或文件夹压缩成 Zip,Jar(略),Gzip(略)的形式
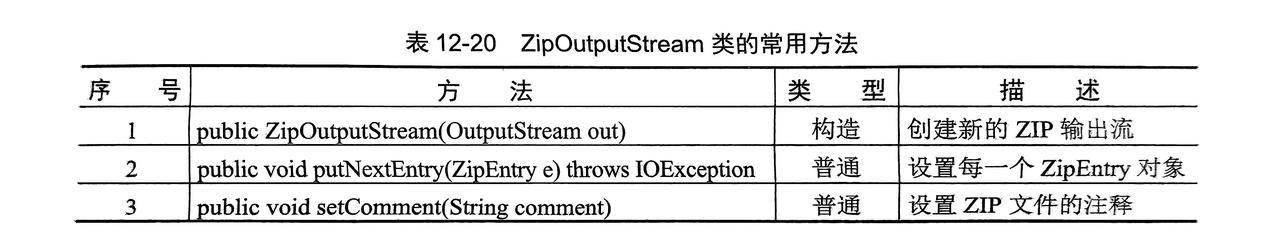
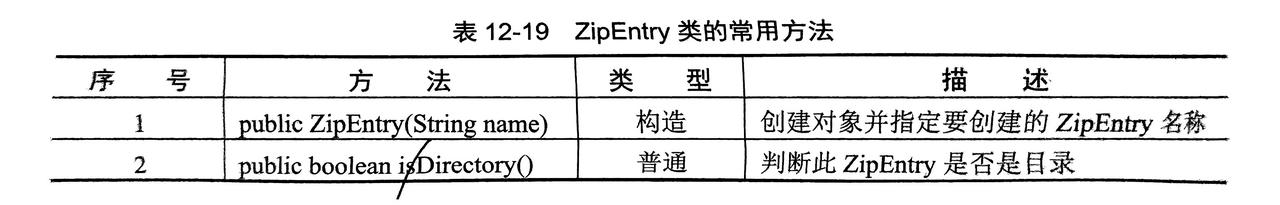
- 压缩成 Zip 主要用到
ZipOutputStream,ZipEntry两个类来完成 - 解压主要用到
ZipFile,ZipInputStream,ZipEntry三个类来完成
压缩步骤:
- 创建
ZipFile的File类(压缩文件存放地址) - 实例化
ZipOutputStream类(压缩包输出类) - 实例化
FileInputStream类(读取需要写入的文件) - 实例化
ZipEntry(压缩子文件对应一个待压缩文件,然后边读边写)
具体代码:如果文件中有文件夹需要修改代码
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 设置需要压缩的文件路径
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io");
// 1. 创建设置zipFile生成压缩包的路径
File zipFile = new File("F:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\zip.zip");
// 3. 实例化InputStream读取数据
InputStream input=null;
// 2. 实例化ZipOutputStream输出类
ZipOutputStream zipOut=new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(zipFile));
if (file.isDirectory()){
// 读取文件夹中所有文件
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
input=new FileInputStream(files[i]);
// 4. 为每个文件实例化ZipEntry,设置文件名
zipOut.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(file.getName()+"_"+files[i].getName()));
int temp=0;
// 一个个读取写入
while ((temp=input.read())!=-1){
zipOut.write(temp);
}
input.close();
}
}
zipOut.close();
}
}14.2 解压
解压步骤:
- 获得压缩包地址,实例化
ZipFile对象 - 实例化
ZipInputStream类(读取压缩包中的子文件,用ZipEntry接收) - 实例化
InputStream类(读取子文件中的数据) - 实例化
OutputStream类(输出生成实体信息)
ZipInputStream类- 可以方便的读取到 Zip 格式下的压缩文件

- 可以方便的读取到 Zip 格式下的压缩文件
ZipFile类- 每一个实例是一个压缩包,对压缩包进行操作
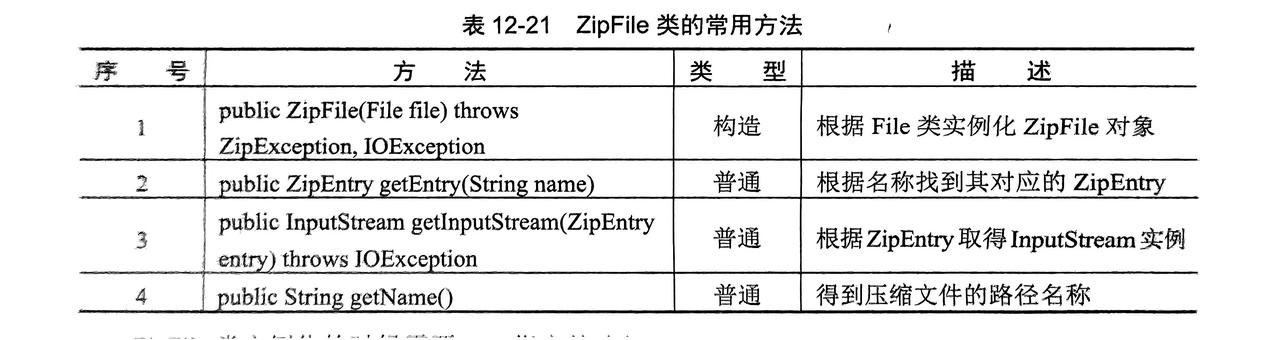
- 每一个实例是一个压缩包,对压缩包进行操作
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 需要解压的压缩包路径
File file = new File("F:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\zip.zip");
// 接收文件的实体
File outFile = null;
// 实例化ZipFile,传入压缩包路径
ZipFile zipFile = new ZipFile(file);
// 实例化ZipInputStream对压缩包进行读取Entry操作
ZipInputStream zipInput = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
// 接收Entry
ZipEntry entry=null;
// 读取Entry中的数据
InputStream input=null;
// 写入到outfile中
OutputStream out=null;
// 遍历所有entry
while ((entry=zipInput.getNextEntry())!=null){
// 每个Entry对应一个文件
outFile=new File("F:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\"+entry.getName());
// 如果没父文件夹创建
if (!outFile.getParentFile().exists()){
outFile.getParentFile().mkdir();
}
if(!outFile.exists()){
outFile.createNewFile();
}
input=zipFile.getInputStream(entry);
out=new FileOutputStream(outFile);
int temp=0;
while ((temp=input.read())!=-1){
out.write(temp);
}
input.close();
out.close();
}
zipInput.close();
zipFile.close();
}
}15. 对象序列化\反序列化
15.1 基本概念与Serialzable接口
- 将对象变为二进制数据流的一种方法
- 需要进行序列化对象的类需要实现Serialzable接口
15.2 对象输出流ObjectOutputStream(序列化)
- 一个对象需要序列化则需要使用ObjectOutputStream进行输出

// 实现Serializable接口
public class User implements Serializable {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public User(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 设置保存路径
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01.txt");
// 实例化OutputStream作为参数实例化ObjectOutputStream
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
User user = new User("张三", 18);
// 序列化对象
objectOutputStream.writeObject(user);
}
}提示
序列化只是把对象属性给序列化在了文件中
因为对象属于同一个类中方法都是一样的,经过反序列化后,只需要获取到属性就可以使用类中的方法
15.3 对象输出流ObjectIntputStream(反序列化)
- 将序列化的文件中的对象反序列化成对象

public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 设置获取路径
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01.txt");
// 实例化InputStream作为参数实例化ObjectInputStream
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
// 分序列化赋值对象
Object obj = objectInputStream.readObject();
User user = (User) obj;
// 依然可以使用类中的方法
System.out.println(user.getName());
}
}15.4 Externalizable接口(了解)
- Serialzable的子接口
- 作用:可以自定义可以需要序列化的属性
接口中两个实现方法:
- writeExternal(ObjectOutput out):指定需要序列化的属性信息,序列化时调用
- readExternal(ObjectOutput out):指定需要反序列化读取的属性信息,反序列化时调用
// 实现Externalizable接口
public class User implements Externalizable {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public User(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 设置需要的序列化信息,调用objectOutputStream序列化时调用此方法
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeObject(this.name);
out.writeInt(this.age);
}
// 设置读取的序列化信息,调用objectIntputStream序列化时调用此方法
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
this.name = (String)in.readObject();
this.age=in.readInt();
}
}
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 设置保存路径
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01.txt");
// 实例化OutputStream作为参数实例化ObjectOutputStream
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
User user = new User("张三", 18);
// 序列化对象
objectOutputStream.writeObject(user);
}
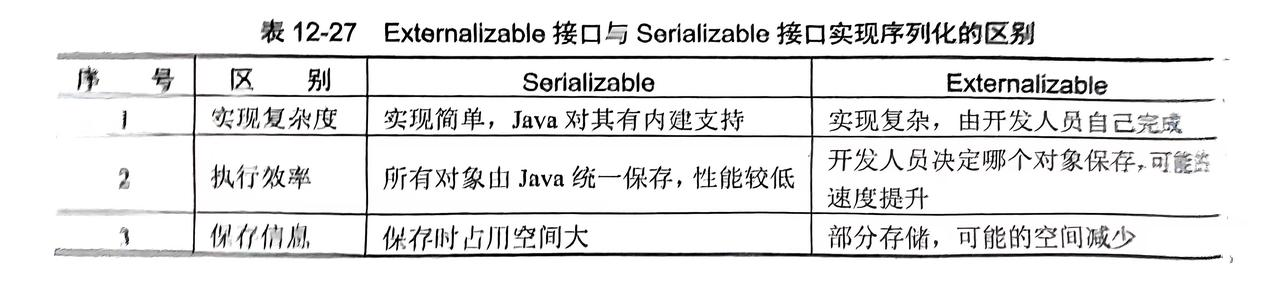
}Serialzable和Externalizable接口的区别?
15.5 transient关键字
- 设置不需要的序列化属性时Externalizable实现起来太麻烦,所以可以使用transient关键字
- 作用:在不需要序列化的属性前加上transient关键字,表示该属性不需要序列化
// 实现Serializable接口
public class User implements Serializable {
// 不需要序列化姓名
private transient String name;
private Integer age;
public User(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}15.6 序列化对象数组
- ObjectOutputStream中只提供writeObject(Object obj)
- 只要明白对象数组也是Object(User[] user也是Object)
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 设置保存路径
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\file01.txt");
// 实例化OutputStream作为参数实例化ObjectOutputStream
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
// 实例化对象数组
User[] users={new User("张三", 18),new User("李四", 21)};
// 序列化对象对象数组
objectOutputStream.writeObject(users);
}
}