2025/9/17大约 6 分钟
Java 类集框架
1. 认识类集(Collection)
- 类集就是动态的对象数组
主要接口: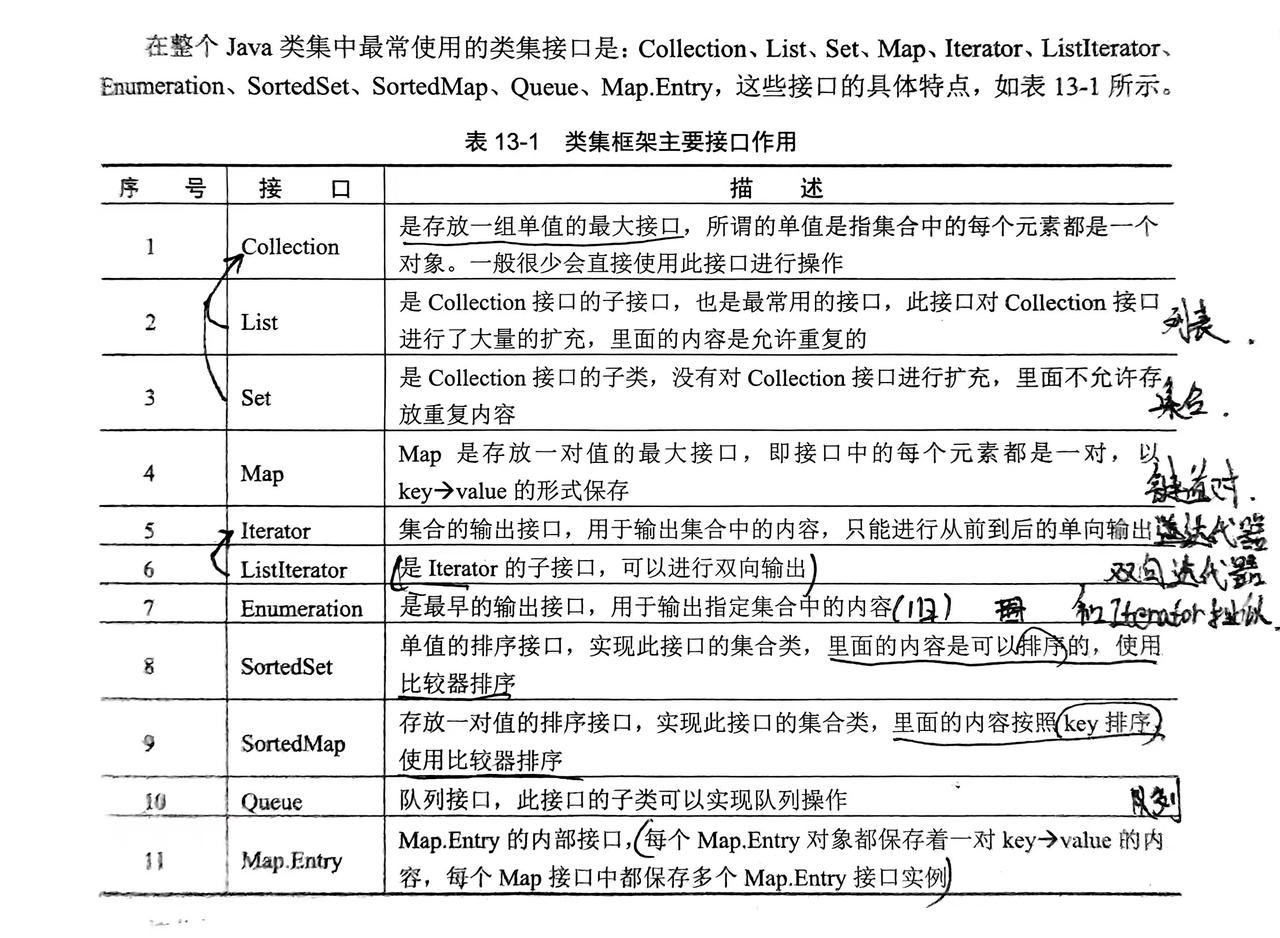
graph TD
Collection --> List
Collection --> Set
Collection --> Queue
Map --> SortedMap继承关系: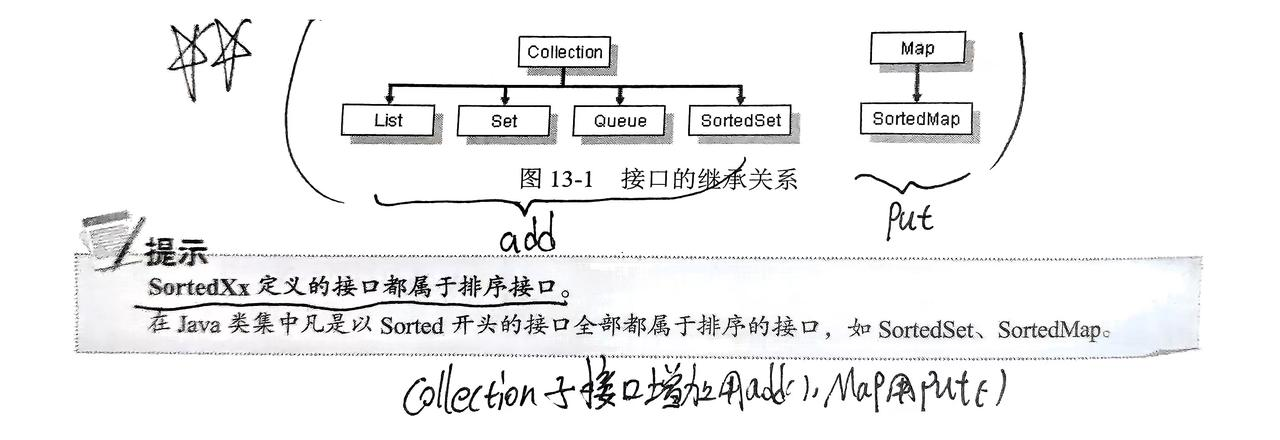
graph TD
Iterable --> Collection
Collection --> List
Collection --> Set
Collection --> Queue
Map --> SortedMapCollection 为单值存放,Map 为键值对存放
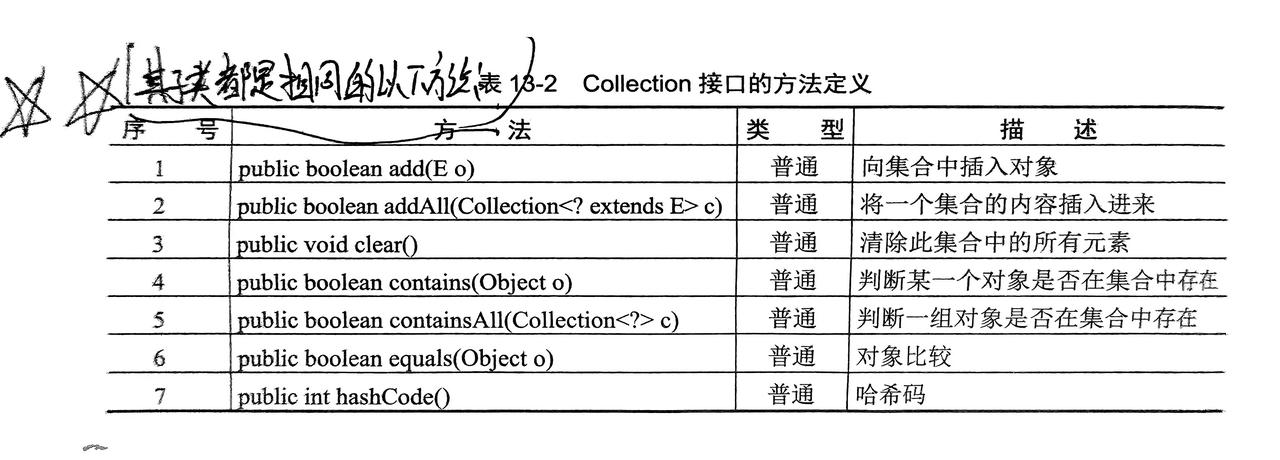
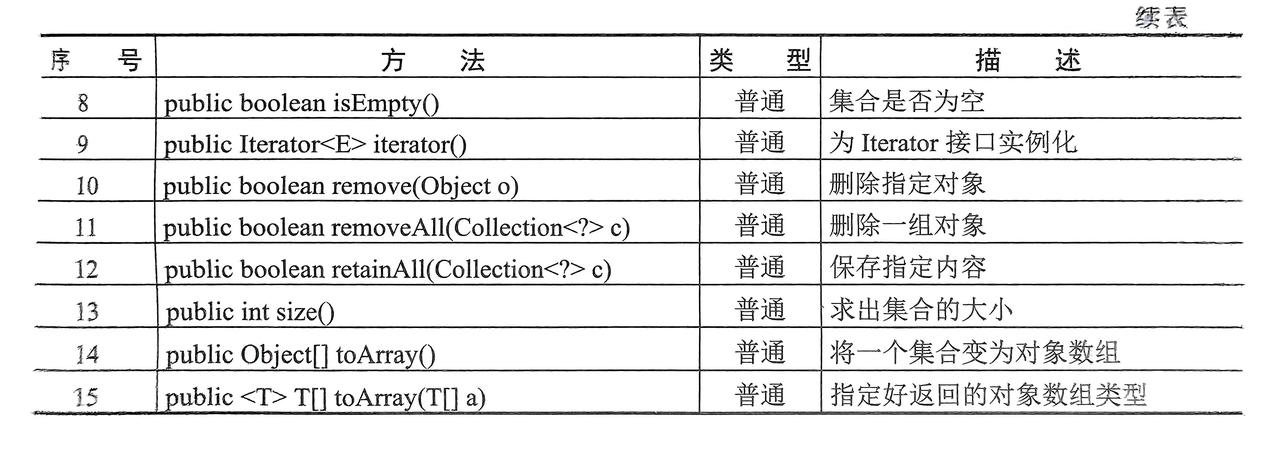
2. Collection接口
- 单值存放的最大接口
提示:
在使用 remove 方法删除指定的对象时,需要在对象类中覆写 hashCode 方法和 equals 方法,才能找到
2.1 List接口(列表)
- 需要子类进行实例化(常用:
ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList(可以同时实例化List和Queue,Queue处介绍))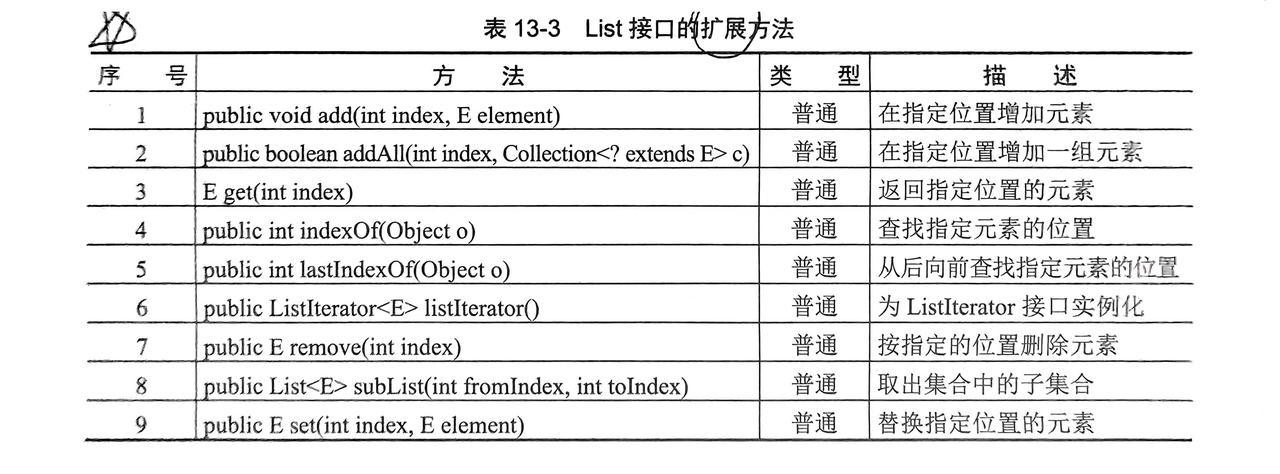
2.1.1 ArrayList和Vector(旧)子类
ArrayList和Vector的用法没有区别,都没拓展方法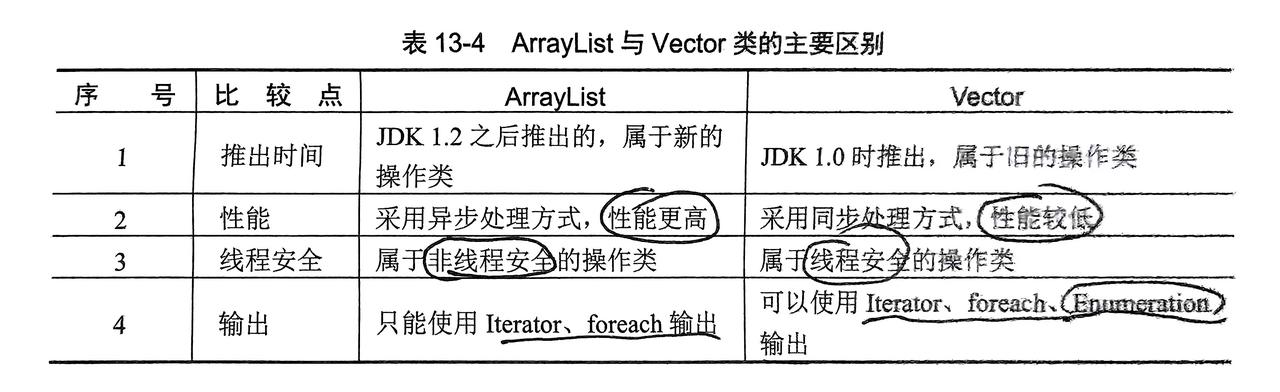
2.2 Queue接口(链表)
- 先进先出的队列
- 需要子类
LinkedList实例化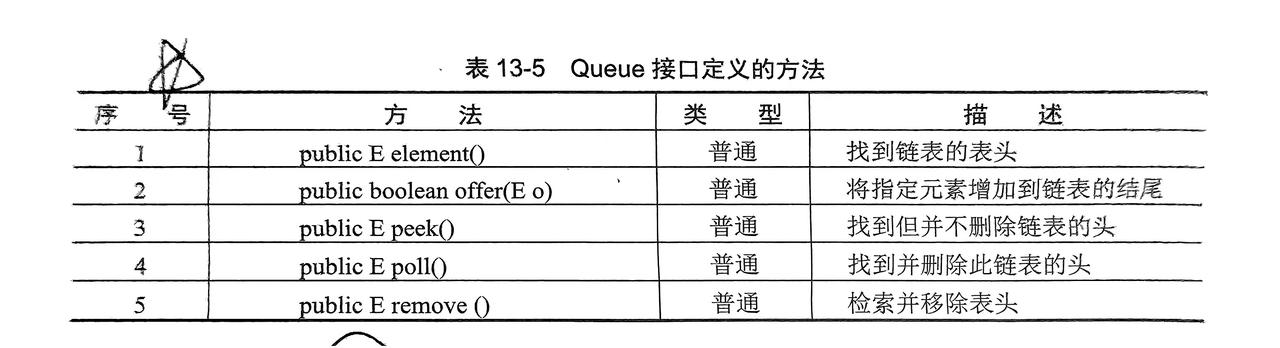
2.2.1 LinkedList子类
- 同时实现了
List,Queue接口,所以List和Queue中的方法都可以使用,且可以分别为两个实例化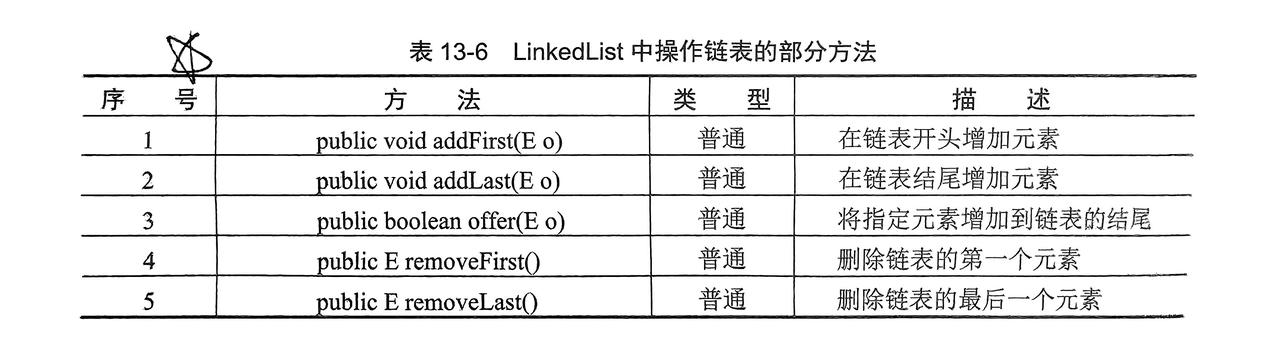
2.3 Set接口(集合)
- 不运行重复元素的集合
- 没有拓展方法,故无精准找到目标元素的方法
- 需要子类进行实例化(常用子类:
HashSet(无序),TreeSet(有序))
2.3.1 HashSet子类
- 特点:不可重复,散列存放,无顺序
- 加入集合的顺序也不是存放顺序
提示:
因为 HashSet 是不可重复的,则在编写自定义类时,需要编写 hashCode 方法和 equals 方法
2.3.2 TreeSet子类
- 特点:不可重复,有顺序
提示:
因为 TreeSet 是不可重复且有顺序,则在编写自定义类时,需要实现 Comparable 接口,编写排序方法
需要注意排序方法的编写需要设计去重
public class User implements Comparable {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public int compareTo(Object o) {
User user=(User) o;
if (this.age>user.age) return 1;
else if (this.age<user.age) return -1;
// 先比对年龄如果相同则调用String中的compareTo比对姓名,只有全部相同才是相同
// 不然会出现仅仅是年龄相同也被判定为重复
else return this.name.compareTo(user.name);
}
}2.4 SortedSet接口(排序集合)
- 也是用
TreeSet子类进行实例化 - 可以看做使用
SortedSet就可以比较精准的对里面的元素进行选取(如获取第一个,最后一个元素等...)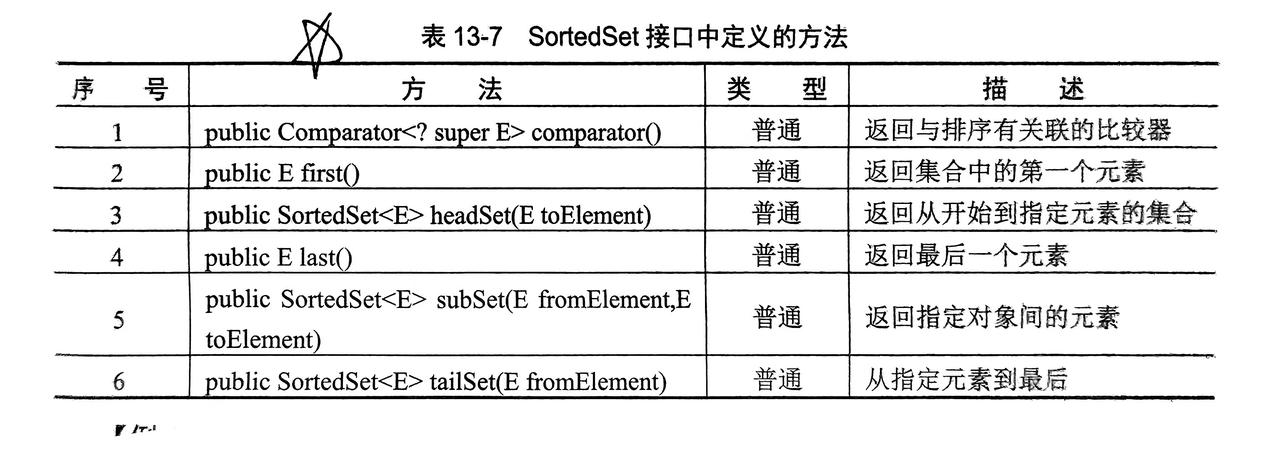
3. 集合的输出
四种输出方式:
Iterator:迭代器ListIterator:双向迭代器Enumeration:功能与Iterator类似,已废弃foreach:1.5后新功能,输出数组和集合
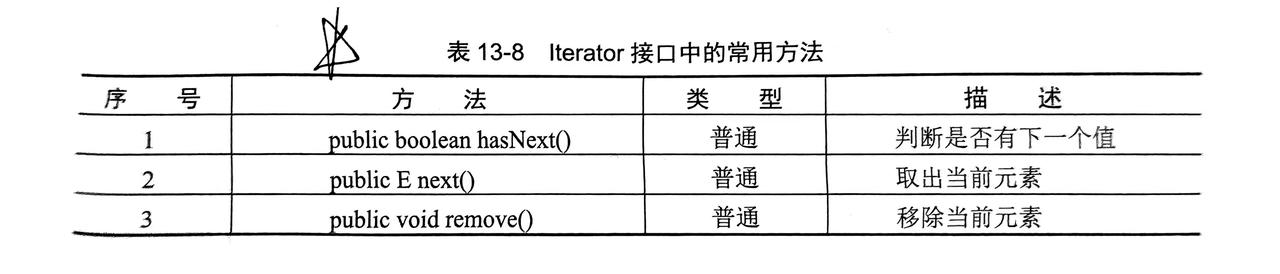
3.1.1 Iterator(迭代器)
- 只要碰到集合的输出,就一定涉及到
Iterator的运用,这是最基本的 - 迭代器模式就是依次判断下一个是否有数据,有就取走
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("b");
// 创建迭代器,所有Collection的子集都是同样的方法
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
String str = iterator.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
}提示:
在调用创建 Iterator 输出时,只能调用迭代器的删除元素(原本的集合会改变),调用集合的删除会报错
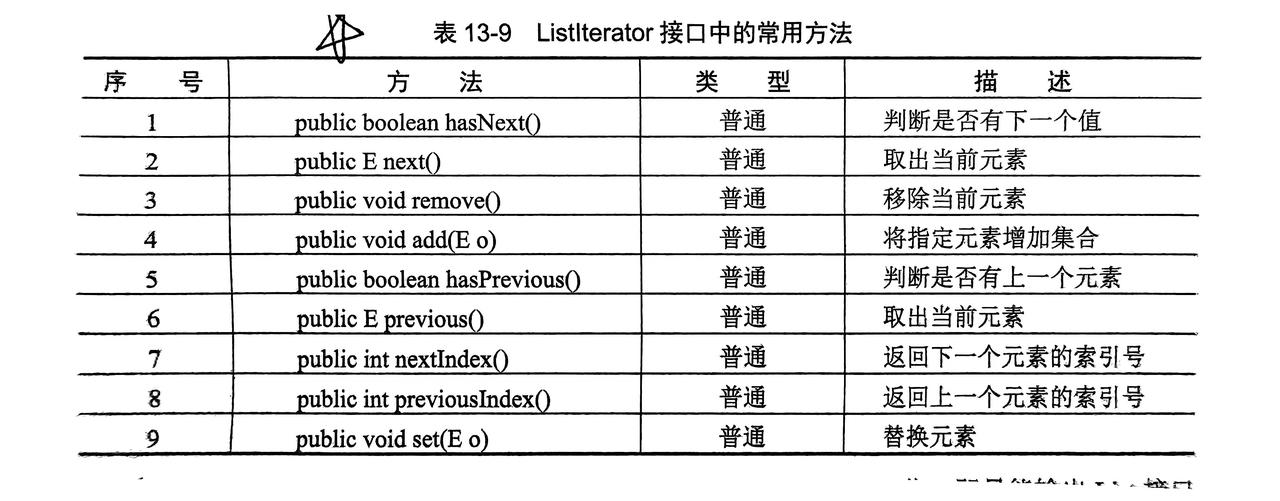
3.1.2 ListIterator(双向迭代器)
Iterator的子接口,只能由List进行实例化- 需要逆向输出时,需要完成一次正向输出
3.1.3 Enumeration(了解)
- 早期和
Vector搭配的迭代器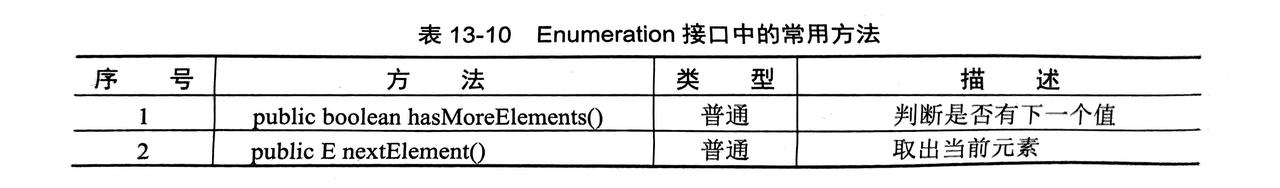
4. Map接口(键值对)
- 需要子类来实例化
a.HashMap/Hashtable(旧):无序存放,key不能重复
b.WeakHashMap:弱引用Map,元素不再使用时,gc进行清除(了解)
c.IdentityHashMap:无序存放,key能重复(针对对象地址)
d.TreeMap:按key有序存放,key不能重复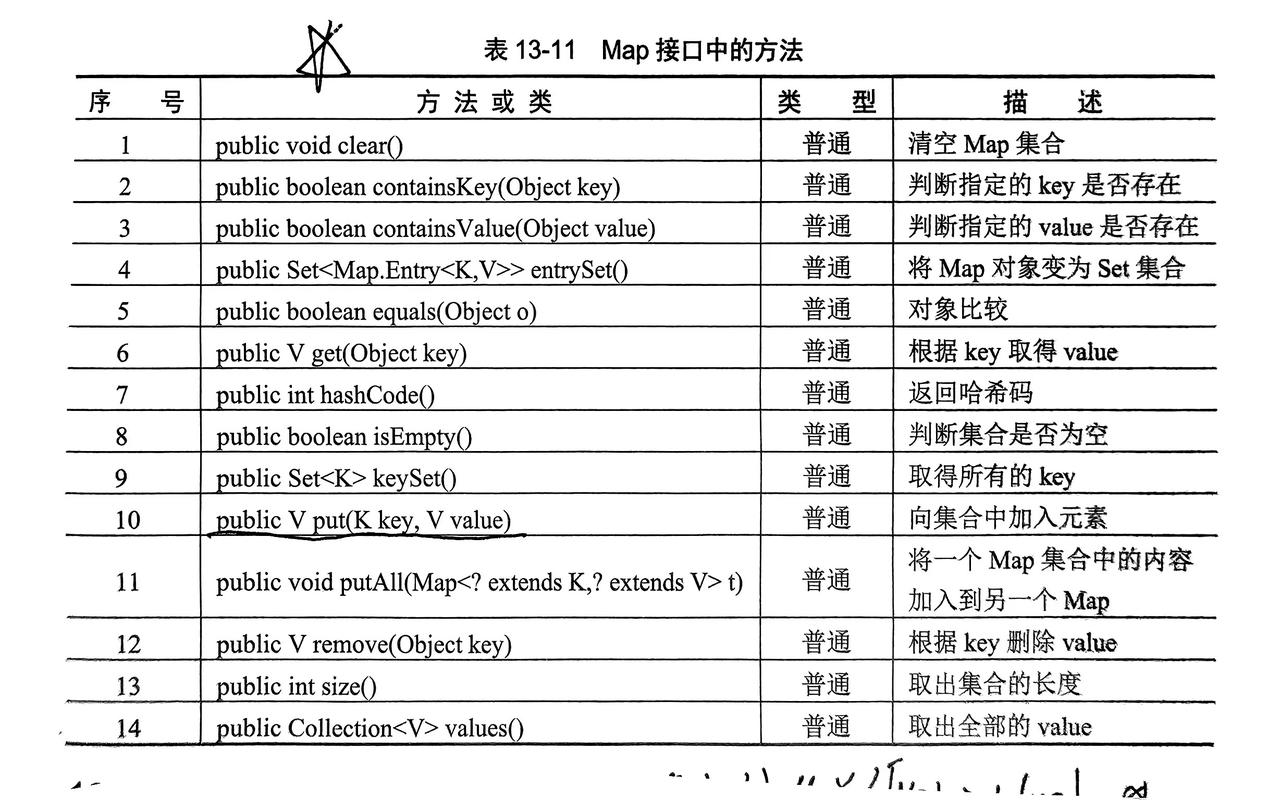
4.1 Map.Entry接口
- 表示
Map集合中的单个的键值对,每put一个map元素就实例化一个Map.Entry - 取出
map元素其实就是取出Map.Entry实例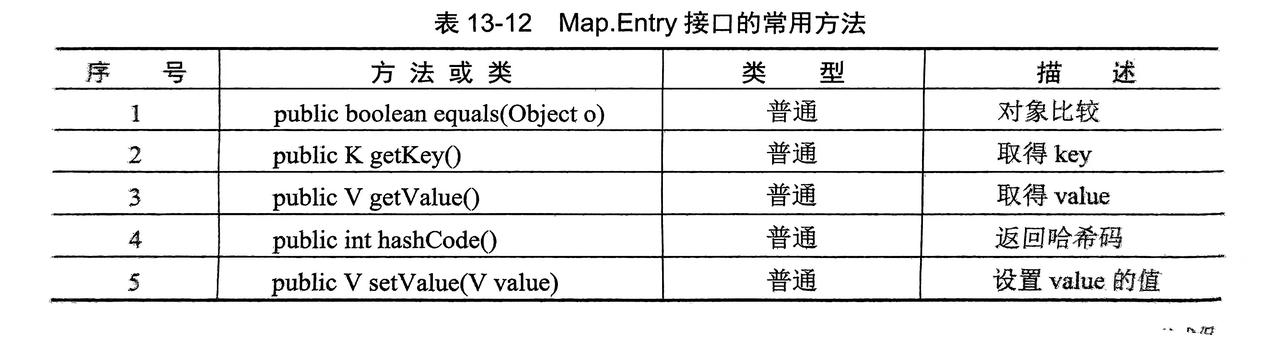
4.2 HashMap/Hashtable(旧)子类
- 无序存放,key不能重复
Hashtable使用方法上和HashMap基本一致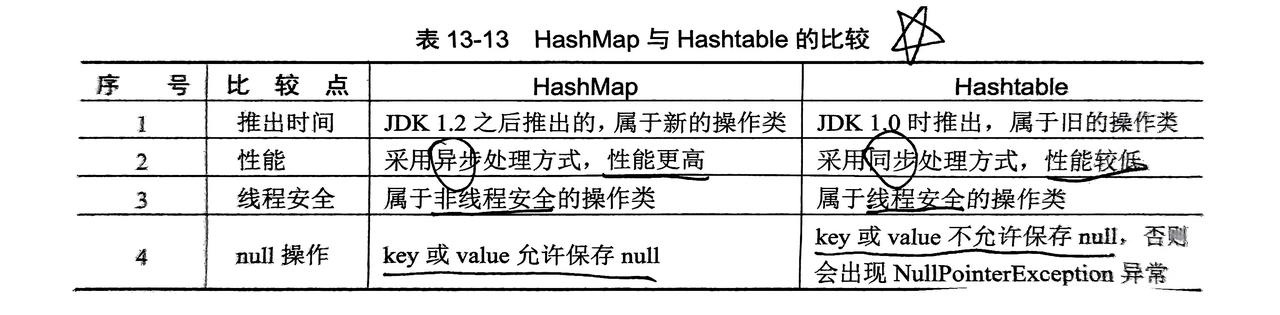
4.3 IdentityHashMap子类
- 无序存放,key能重复(针对对象地址)
- 只要key为对象,且两个的对象的地址不一样(内容相同),就可以重复
4.4 TreeMap子类
- 按key有序存放,key不能重复
- 同
TreeSet一样,key是自定义对象时,需要实现Comparable接口,自己编写排序方法
4.5 Map的注意事项
4.5.1 不能迭代输出Map集合
- 不能使用
iterator,foreach输出:因为上述方法都只能获取到单个值 - 若要使用则需要将
Map转换为元素为Map.Entry的Set集合
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,3);
map.put(3,5);
map.put(5,7);
// 将map中的Entry装换为Set集合
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
// Set创建迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> iterator = entries.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next.getValue());
}
// foreach方法,增强for
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> next:entries){
System.out.println(next.getValue());
}
}
}4.5.2 对象作为key时注意
- 一定要覆写
hashCode方法和equals方法
4.6 SortedMap(排序键值对)
- 也是用
TreeMap子类进行实例化 - 可以看做使用
SortedMap就可以比较精准的对里面的键值对进行选取(如获取第一个,最后一个键值对等...)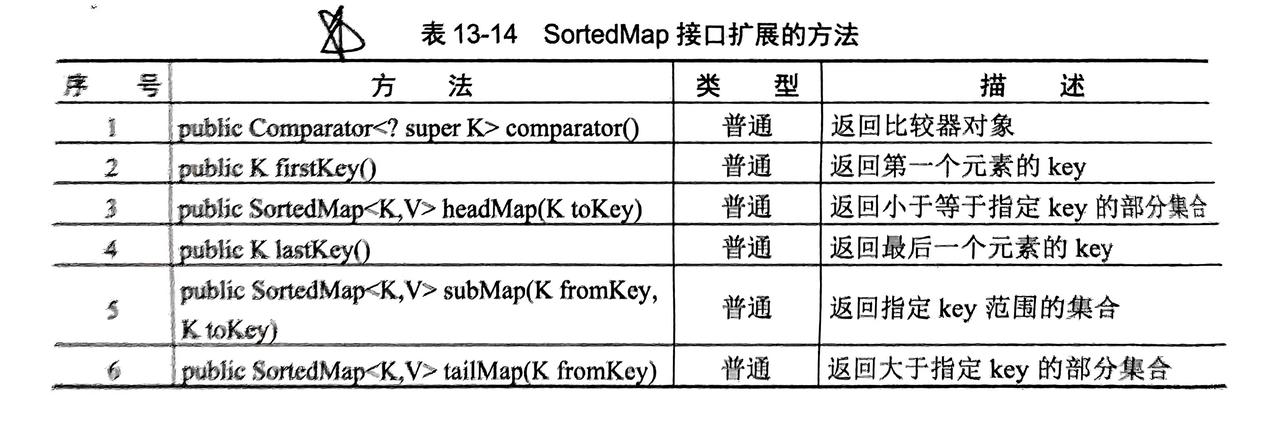
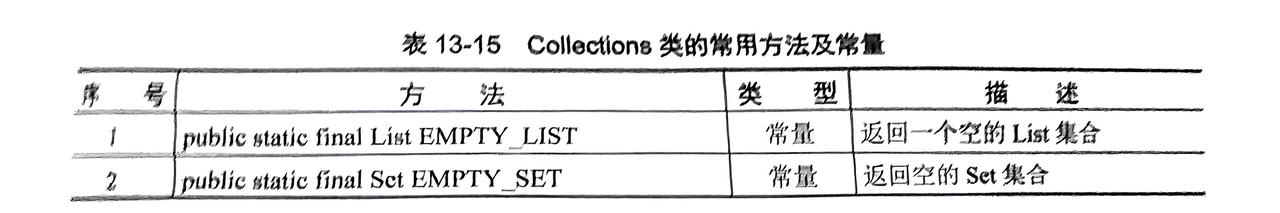
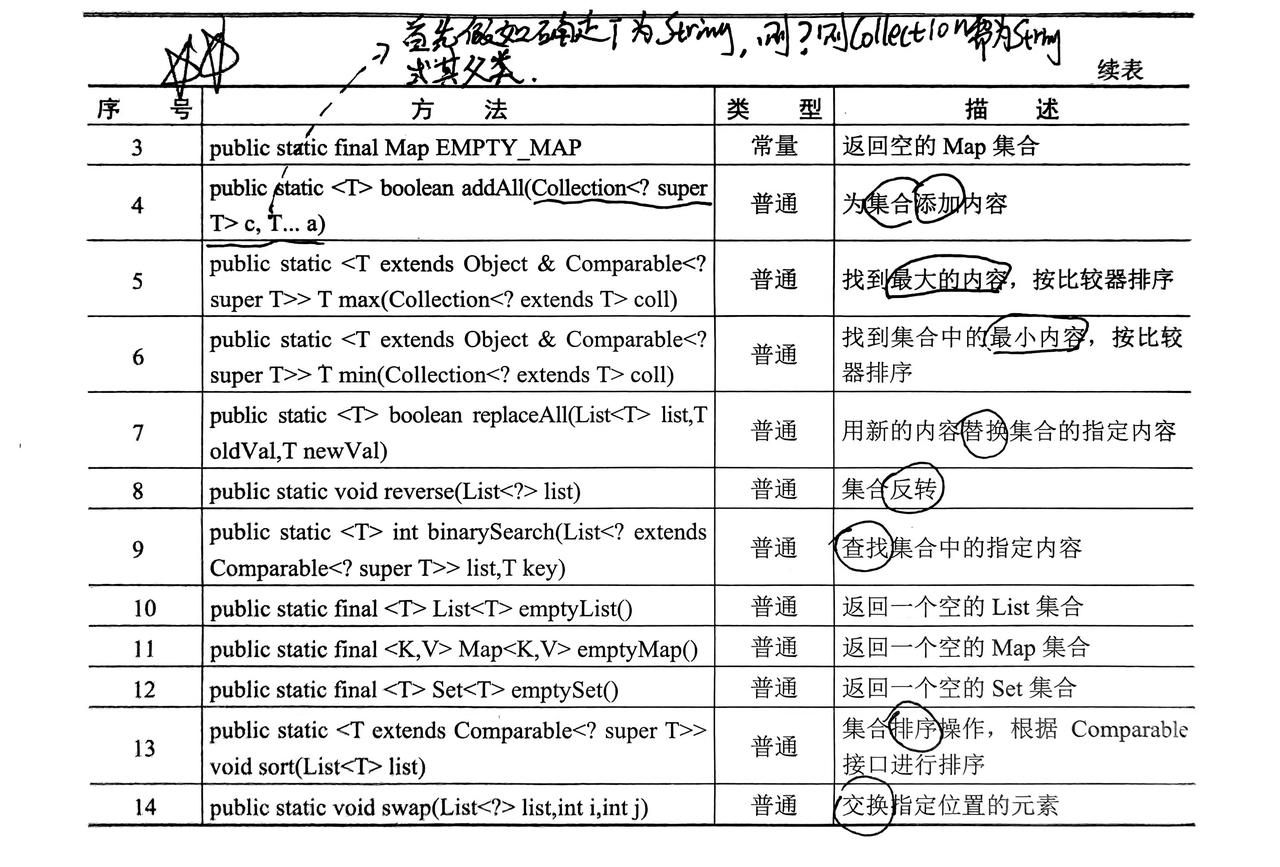
5. 集合工具类Collections类
- 对上述集合提供一些简便方法
- 该类是内部方法都是静态方法,自己使用类名调用
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,1,2,3);
}
}6. 其他集合类
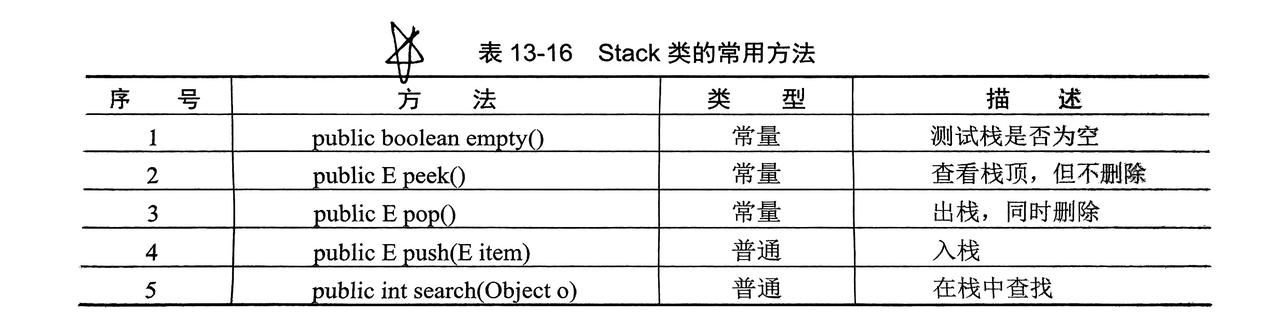
- 在
Vector类派生出子类Stack类(栈) - 在
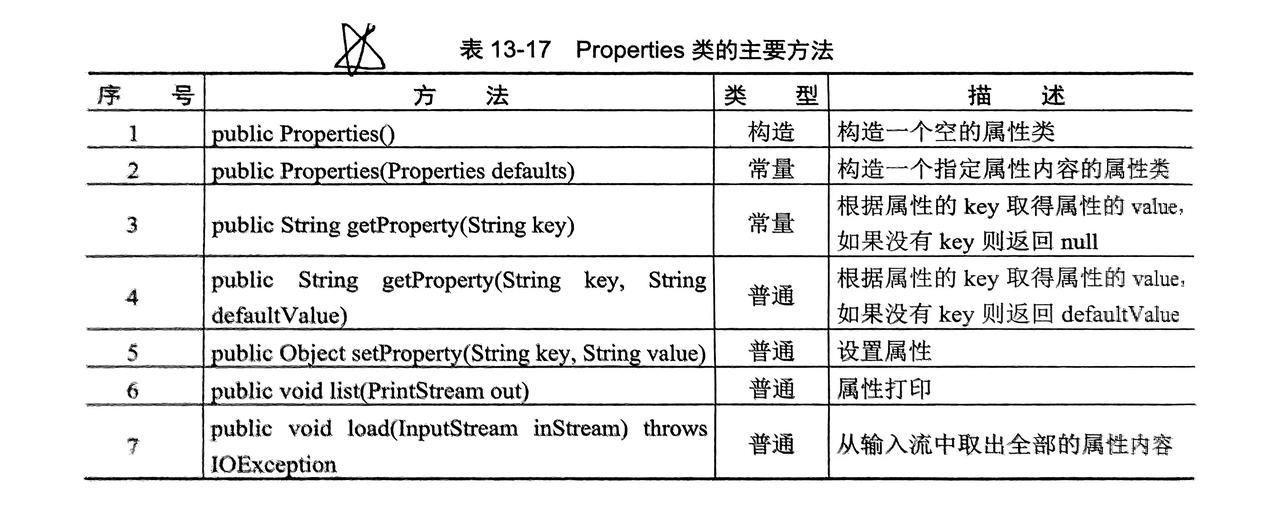
HashMap类派生出子类Properties类(属性操作)
6.1 Stack子类
- 先进后出
6.2 Properties子类
- 对
*.properties后缀的属性文件进行操作 - 可以结合 IO 进行输出和读取
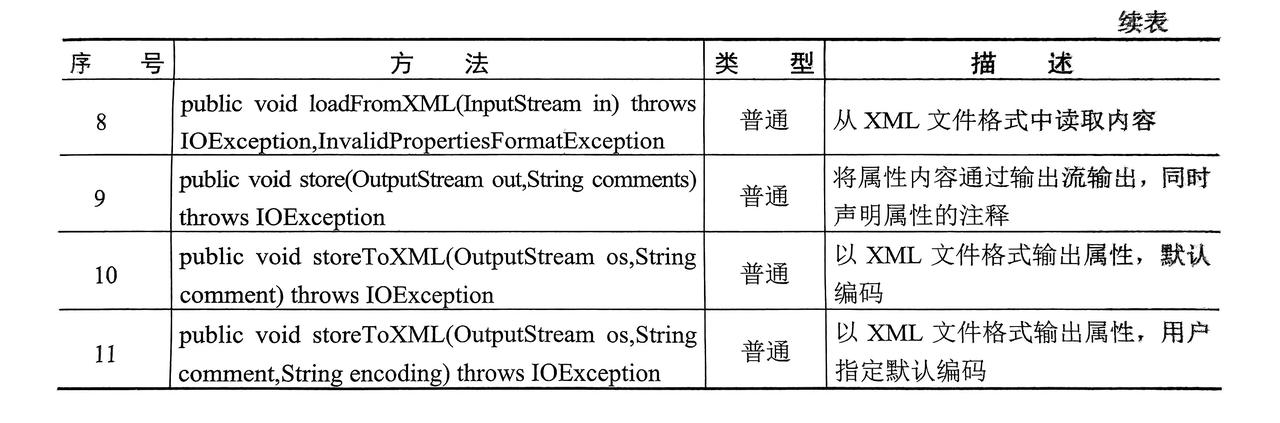
- 获取,修改属性:
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.实例化Properties类
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2.设置需要读取的properties文件
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\mysql.properties");
// 3.添加输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 4.将获取到的配置信息输入到properties对象中
properties.load(fis);
fis.close();
// 获取,修改数据
String data = properties.getProperty("user");
properties.setProperty("user","cmx");
System.out.println(data);
}
}- 添加属性文件:
public class dome01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.实例化Properties类
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2.设置需要写入的properties文件
File file = new File("F:\\Code\\IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.5\\yuancode\\untitled1\\src\\io\\mysql.properties");
// 3.添加输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 4.需要写入文件的属性
properties.setProperty("add","addData");
// 5.将添加的配置信息输入到properties文件中
properties.store(fos,"zhushi");
fos.close();
String data = properties.getProperty("add");
System.out.println(data);
}
}