Spring Cloud Gateway 基础入门
前置知识
在开始本教程之前,建议您具备以下基础知识:
- Java 基础语法
- Spring Boot 基础
- Spring Cloud 基本概念
- 微服务架构基础
什么是 Spring Cloud Gateway?
Spring Cloud Gateway 是 Spring Cloud 的一个全新项目,基于 Spring 5.0、Spring Boot 2.0 和 Project Reactor 等技术开发的网关,它旨在为微服务架构提供一种简单有效的 API 路由管理方式。
Spring Cloud Gateway 作为 Spring Cloud 生态系统中的网关,目标是替代 Netflix Zuul,其不仅提供统一的路由方式,并且基于 Filter 链的方式提供了网关基本的功能,例如:安全、监控/指标、限流等。
核心特性
- 基于 Spring Framework 5、Project Reactor 和 Spring Boot 2.0
- 动态路由:能够匹配任何请求属性
- 集成 Spring Cloud DiscoveryClient
- Predicates 和 Filters 作用于特定路由
- 内置多种 Predicates 和 Filters
- 易于编写的 Predicates 和 Filters
- 请求限流
- 路径重写
- 支持 WebSocket
Gateway 与 Zuul 的对比
在了解 Spring Cloud Gateway 之前,我们先来看看它与 Netflix Zuul 的区别:
| 特性 | Spring Cloud Gateway | Netflix Zuul 1.x |
|---|---|---|
| 架构模型 | 异步非阻塞 | 同步阻塞 |
| 底层实现 | Netty + WebFlux | Servlet |
| 性能 | 高 | 中 |
| 限流 | 内置支持 | 需要集成其他组件 |
| 动态路由 | 支持 | 支持但较复杂 |
| 负载均衡 | 集成 Ribbon | 集成 Ribbon |
| 熔断降级 | 集成 Resilience4j/Hystrix | 集成 Hystrix |
| 上手难度 | 中等 | 简单 |
| Spring 5 特性支持 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| WebSocket 支持 | 支持 | 有限支持 |
注意
Netflix Zuul 2.x 也采用了异步模型,但 Spring Cloud 官方已经明确推荐使用 Spring Cloud Gateway 作为首选网关实现。
Gateway 核心概念
Spring Cloud Gateway 的核心概念主要包括以下三个部分:
1. 路由(Route)
路由是网关的基本组成部分。它由 ID、目标 URI、Predicate 集合和 Filter 集合组成。如果 Predicate 为真,则路由匹配,目标服务会被访问。
2. 断言(Predicate)
这是一个 Java 8 的 Predicate 函数。输入类型是 Spring Framework ServerWebExchange。我们可以使用它来匹配 HTTP 请求中的任何内容,例如 headers 或参数。
3. 过滤器(Filter)
这些是 Spring Framework GatewayFilter 的实例,我们可以使用它们修改请求和响应。
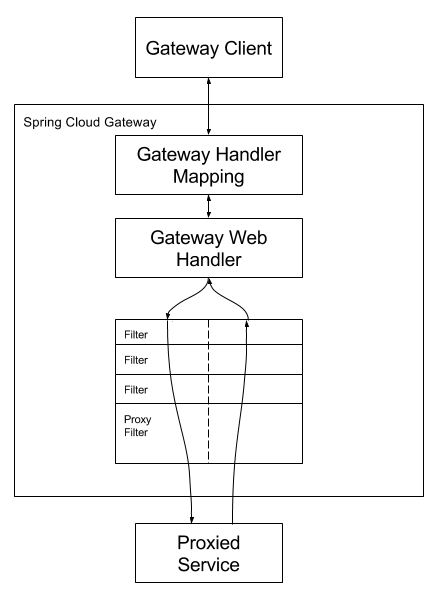
工作原理
Spring Cloud Gateway 的工作流程如下:
- 客户端向 Spring Cloud Gateway 发出请求
- Gateway Handler Mapping 确定请求与路由匹配(使用 Predicate)
- 请求经过 Gateway Web Handler 处理
- Web Handler 将请求交给一个过滤器链,其中包含特定路由的过滤器
- 前置过滤器(Pre Filters)在请求被发送到目标服务之前执行
- 请求被发送到目标服务
- 后置过滤器(Post Filters)在收到目标服务的响应后执行
- 响应返回给客户端
环境准备
1. 添加依赖
在您的 pom.xml 中添加 Spring Cloud Gateway 相关依赖:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2021.0.5</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Cloud Gateway -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Boot Actuator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>注意
由于 Spring Cloud Gateway 是基于 Spring WebFlux 的,所以不要引入 spring-boot-starter-web 依赖,否则会导致应用无法启动。
2. 创建项目结构
src/main/java/com/example/gateway/
├── GatewayApplication.java
└── config/
└── RouteConfig.java3. 配置文件
创建 application.yml 文件:
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: example-route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Path=/example/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: gateway,health,info基本使用
1. 启动类
package com.example.gateway;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class GatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GatewayApplication.class, args);
}
}2. 路由配置
基于配置文件的路由
在 application.yml 中配置路由:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: service-a
uri: http://localhost:8081
predicates:
- Path=/service-a/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
- id: service-b
uri: http://localhost:8082
predicates:
- Path=/service-b/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1基于 Java 代码的路由
package com.example.gateway.config;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteLocator;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.builder.RouteLocatorBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RouteConfig {
@Bean
public RouteLocator customRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("service-a", r -> r.path("/service-a/**")
.filters(f -> f.stripPrefix(1))
.uri("http://localhost:8081"))
.route("service-b", r -> r.path("/service-b/**")
.filters(f -> f.stripPrefix(1))
.uri("http://localhost:8082"))
.build();
}
}路由断言工厂
Spring Cloud Gateway 内置了许多路由断言工厂,用于匹配 HTTP 请求的不同属性。以下是一些常用的断言工厂:
1. Path 路由断言工厂
匹配请求路径:
predicates:
- Path=/api/users/{segment},/api/orders/{segment}2. Method 路由断言工厂
匹配 HTTP 方法:
predicates:
- Method=GET,POST3. Host 路由断言工厂
匹配主机名:
predicates:
- Host=**.example.org,**.example.com4. Header 路由断言工厂
匹配请求头:
predicates:
- Header=X-Request-Id, \d+5. Query 路由断言工厂
匹配查询参数:
predicates:
- Query=username, \w+6. Cookie 路由断言工厂
匹配 Cookie:
predicates:
- Cookie=sessionId, \d+7. After/Before/Between 路由断言工厂
基于时间的匹配:
predicates:
- After=2023-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]
- Before=2023-01-21T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]
- Between=2023-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver], 2023-01-21T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]过滤器工厂
Spring Cloud Gateway 内置了多种过滤器工厂,用于修改请求和响应。以下是一些常用的过滤器工厂:
1. AddRequestHeader 过滤器工厂
添加请求头:
filters:
- AddRequestHeader=X-Request-Id, 1232. AddResponseHeader 过滤器工厂
添加响应头:
filters:
- AddResponseHeader=X-Response-Id, 4563. StripPrefix 过滤器工厂
去除请求路径前缀:
filters:
- StripPrefix=14. PrefixPath 过滤器工厂
添加请求路径前缀:
filters:
- PrefixPath=/api5. RequestRateLimiter 过滤器工厂
请求限流:
filters:
- name: RequestRateLimiter
args:
redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 10
redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 20实际案例:构建简单的 API 网关
下面我们将构建一个简单的 API 网关,它将请求路由到不同的后端服务。
1. 配置文件
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: user-service
uri: http://localhost:8081
predicates:
- Path=/api/users/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
- AddRequestHeader=X-Gateway-Source, api-gateway
- id: order-service
uri: http://localhost:8082
predicates:
- Path=/api/orders/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
- AddResponseHeader=X-Gateway-Response-Time, ${now}2. 自定义过滤器
自定义全局过滤器示例
package com.example.gateway.filter;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilterChain;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GlobalFilter;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@Component
public class LoggingGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggingGlobalFilter.class);
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
logger.info("Path requested: {}", exchange.getRequest().getPath());
return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> {
logger.info("Response status: {}", exchange.getResponse().getStatusCode());
}));
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return -1; // 设置过滤器的优先级,数字越小优先级越高
}
}3. 自定义路由断言工厂
自定义路由断言工厂示例
package com.example.gateway.predicate;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.AbstractRoutePredicateFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
@Component
public class UserAgentRoutePredicateFactory extends AbstractRoutePredicateFactory<UserAgentRoutePredicateFactory.Config> {
public UserAgentRoutePredicateFactory() {
super(Config.class);
}
@Override
public Predicate<ServerWebExchange> apply(Config config) {
return exchange -> {
String userAgent = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders().getFirst("User-Agent");
return userAgent != null && userAgent.contains(config.getAgent());
};
}
@Override
public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() {
return Arrays.asList("agent");
}
public static class Config {
private String agent;
public String getAgent() {
return agent;
}
public void setAgent(String agent) {
this.agent = agent;
}
}
}总结
本文介绍了 Spring Cloud Gateway 的基本概念、核心特性以及与 Zuul 的对比。我们学习了如何配置 Gateway 的路由、断言和过滤器,并通过一个简单的案例了解了 Gateway 的实际应用。
Spring Cloud Gateway 作为新一代的 API 网关,具有高性能、非阻塞、易于扩展等特点,是微服务架构中不可或缺的组件。
下一步学习
- 学习 Spring Cloud Gateway 的高级特性
- 了解如何将 Gateway 与服务发现组件集成
- 探索 Gateway 的限流、熔断等高级功能
希望这个教程对您有所帮助!如果您有任何问题,欢迎在评论区讨论。
